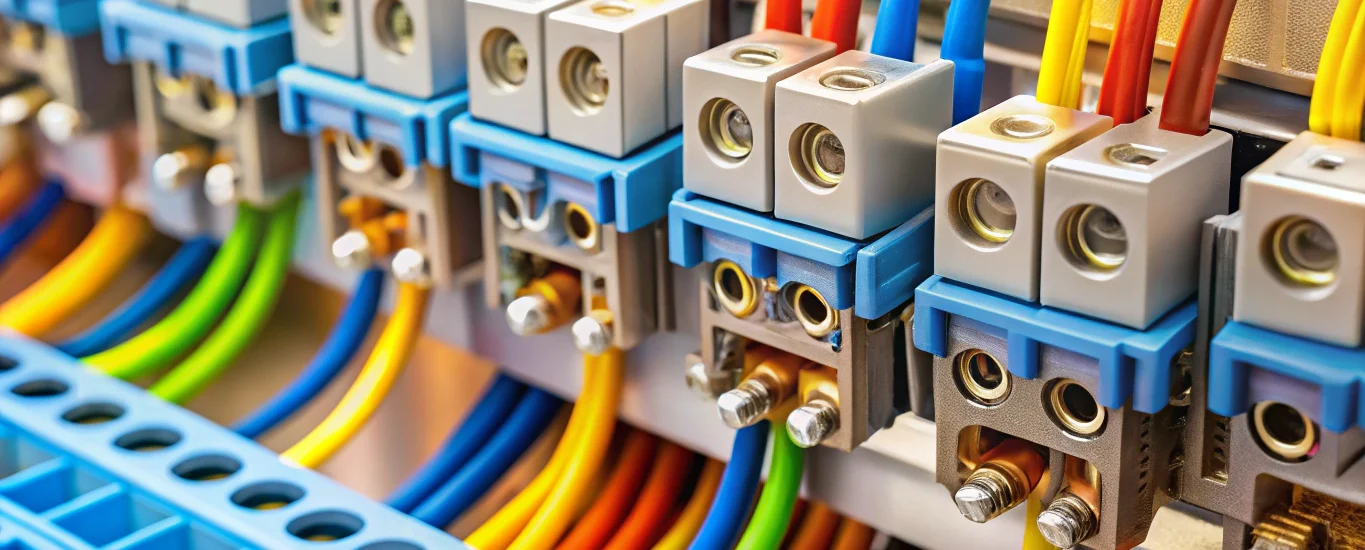
In the intricate dance of modern electrical systems, electrical connectors play a pivotal role, seamlessly linking conductors to ensure power flows reliably and safely.
The Heartbeat of Electrical Systems
Connectors serve as the vital junctions within any electrical network. Without them, circuits would remain disjointed, leading to inefficiencies, safety hazards, and system failures. By providing secure, conductive interfaces, connectors uphold the integrity of electrical installations across residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
A Symphony of Connector Types
Diverse in design and function, electrical connectors come in forms tailored to specific needs. Here are some of the most common:
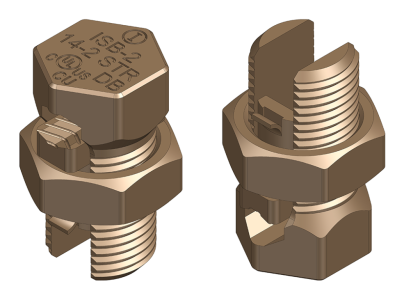
- Crimp Connectors: These connectors rely on a deformative process that compresses a metal sleeve around the cable conductor. For best practices, consult the Guide to Crimping from TE Connectivity and explore our Copper Compression Type “C” Crimp Connectors.
- Mechanical Connectors: Utilizing screws or clamps to secure conductors, these connectors offer easy installation and adjustability. Learn more in our Mechanical Connectors Overview.
- Ring Lugs: Ideal for bolted terminations, ring lugs provide a robust mechanical and electrical bond. Discover our Tinned Copper Ring Type Cable Terminal Ends.
- Split Bolts: Offering a reliable splice, split bolts clamp conductors together under high compression. Browse our Copper Split Bolt Connectors.
For the full variety of solutions, explore our Full Connectors Range.
The Versatility of Electrical Connectors
From heavy-duty power distribution to delicate signal transmission, connectors adapt to a vast array of voltage levels, temperatures, and environmental conditions. Detailed specifications, such as insulation material and conductor compatibility, ensure each connector meets the precise demands of its application. For an in-depth reference on wire ranges, see the Ideal Industries Wire Connector Guide.
Tools of the Trade
Interactive Calculators
Quickly determine conductor sizes, voltage drops, and torque settings with online tools like the Southwire Calculators, streamlining design and installation processes.
Quality Materials
Selecting top-grade alloys and housings enhances durability and conductivity. Studies such as the 3M Connector Comparison Study highlight performance differentials between shear and compression crimps.
Crafting the Perfect Connection: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Strip Conductors: Remove insulation to the specified length without nicking strands.
- Choose Connector Type: Match connector style to cable gauge and application.
- Insert Conductor: Fully seat strands into the connector barrel.
- Apply Compression: Use calibrated crimping tools or torque wrenches per manufacturer guidelines.
- Inspect Joint: Verify mechanical stability and electrical continuity with a pull test and multimeter.
- Insulate & Secure: Add heat-shrink tubing or insulating boots, then secure cables to prevent movement.
Navigating Common Challenges
- Oxidation from moisture exposure.
- Loose terminations due to insufficient torque.
- Over-compressed strands reducing conductivity.
- Incompatible materials causing galvanic corrosion.
The Art of Informed Choices
Balancing cost, performance, and longevity means evaluating connector specifications against project requirements. Whether you prioritize ease of installation or maximum conductivity, our Complete Connectors Range offers tailored solutions backed by technical support.